Electric Vehicle in Nepal 2025 | Prices, Benefits, Charging & Future Trends
For more than a century, the familiar roar of the combustion engine has dominated our roads. But a quiet revolution is underway, gradually replacing that noise with a smooth, almost silent hum. Electric Vehicle (EV) are no longer futuristic concepts confined to laboratories. They are here, practical, and reshaping how we think about mobility. With rising environmental concerns, advancements in battery technology, and growing global adoption, EVs are paving the way toward cleaner, smarter, and more efficient transportation.
History of Electric Vehicle
EVs may seem like a modern innovation, but their roots go back nearly two centuries. In the 1830s, the first crude electric carriages appeared, and by the late 1800s, EVs were already competing with steam and gasoline-powered cars. Early electric cars were quiet, easy to drive, and even held land speed records.
However, the discovery of cheap petroleum, combined with Charles Kettering’s invention of the electric starter in 1912 and Henry Ford’s mass production of the affordable Model T, shifted the market in favor of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. For most of the 20th century, EVs disappeared from mainstream roads.
The oil crises of the 1970s revived some interest, but only in the late 1990s and early 2000s did EVs start gaining real traction. Growing awareness of climate change, stricter emissions standards, and advances in battery technology reignited global efforts. Tesla’s launch of the Roadster in 2008 demonstrated that EVs could be stylish, high-performance, and practical igniting the modern EV revolution.
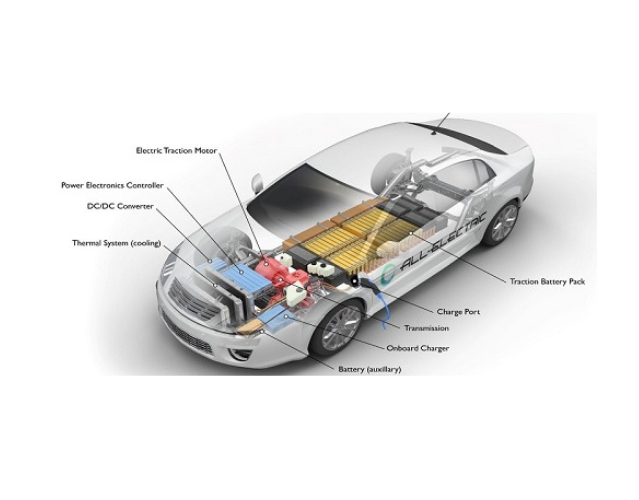
How Electric Vehicle Works
At their core, EVs are simpler than petrol or diesel cars. They replace the complexity of an internal combustion engine with an electric motor powered by rechargeable batteries.
Key Components:
- Battery Pack (Traction Battery): Stores electricity, functioning as the fuel tank.
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical motion to drive the wheels.
- Power Electronics Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity, managing speed and torque.
- Onboard Charger: Converts AC power from charging stations into DC power for the battery.
- Regenerative Braking: Captures energy during braking and feeds it back to the battery.

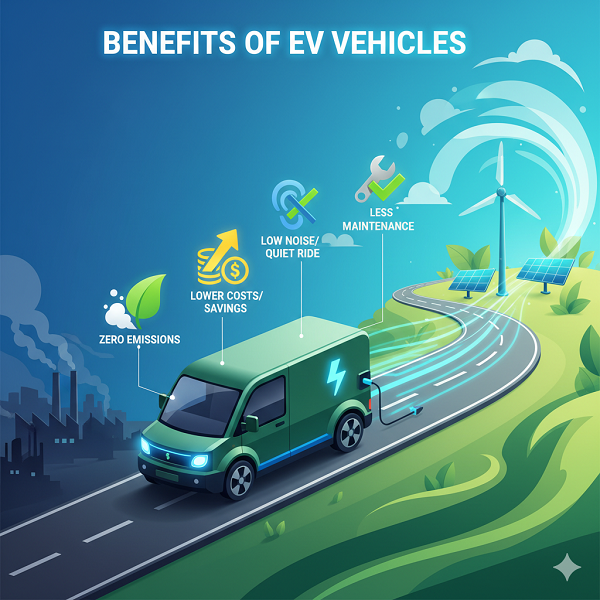
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions: Reduces greenhouse gases and improves urban air quality.
- Lower Running Costs: Electricity is cheaper than fuel; fewer parts mean lower servicing costs.
- Quiet & Smooth Drive: Minimal vibration and noise improve driving comfort.
- High Performance: Instant torque ensures rapid acceleration.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs use over 75% of input energy for motion, compared to ~25% for petrol cars
Electric Van vs Petrol Van Cost

Battery Lifetime and Sustainability
- Typical Lifespan: Modern electric car batteries are designed for durability, generally maintaining sufficient capacity for 10-15 years of typical use, often outlasting the vehicle itself.
- Extended Utility through Second-Life Applications: After their automotive service, batteries can be repurposed for less demanding roles, such as storing energy from solar panels for homes or businesses, thereby extending their useful life for many more years.
- Closing the Loop with Recycling: A growing recycling industry is focused on creating a circular economy for batteries. Processes are being developed to efficiently break down end-of-life units and extract valuable raw materials to manufacture new batteries.
- Maximizing Battery Health: Owners can optimize their battery's longevity by following simple practices: avoiding constant full charges or complete discharges, minimizing exposure to extreme heat, and using rapid-charging stations primarily for long trips rather than daily use.
EV van vs Petrol Van Cost in Nepal
Assumptions (2025):
- Petrol price (Kathmandu): NPR 161/liter
- Electricity rate (residential): NPR 9/kWh
- Average fuel vehicle mileage: 12 km/L
- Average EV consumption: 15 kWh/100 km
- Annual distance: 15,000 km/year
Running Cost Comparison:
|
Time Period |
Petrol Vehicle (NPR) |
Electric Vehicle (NPR) |
|
1 Year |
226,250 |
28,250 |
|
5 Years |
1,131,250 |
141,250 |
|
10 Years |
2,262,500 |
282,500 |
10 Electric Vehicles Price
|
EV Model |
Listed Price (NPR) |
|
|
1 |
Tata Tigor EV (base) |
Rs. 2,499,000 |
|
2 |
Nexon EV (Prime XM) |
Rs. 3,899,000 |
|
3 |
BYD Dolphin |
Rs. 4,115,000 |
|
4 |
BYD Atto 3 |
Rs. 5,690,000 |
|
5 |
Hyundai Kona Electric |
Rs. 5,700,000 – 7,200,000 |
|
6 |
MG S5 EV |
Rs. 4,400,000 – 5,500,000 |
|
7 |
Rs. 3,599,000 |
|
|
8 |
Contact Triveni Motocorp |
|
|
9 |
Contact Triveni Motocorp |
|
|
10 |
Contact Triveni Motocorp |
Charging Station Infrastructure
The availability of convenient charging is critical for EV adoption.
Types of Charging:
- Level 1 (Slow): Standard household socket, best for overnight charging.
- Level 2 (Fast): 240V outlets at homes, offices, and public stations; faster and practical.
- DC Fast Charging (Rapid): High-powered charging, adding hundreds of kilometers in under an hour—ideal for highways.
Charging Diagram

Global Adoption & Market Trends
EV adoption is accelerating worldwide:
- China leads in manufacturing and sales, with brands like BYD and NIO.
- Europe (Norway, Germany, UK ) is rapidly phasing out ICE sales with strict emission targets
- USA sees Tesla dominating but faces strong competition from Ford, GM, Rivian, and Lucid.
- India & Southeast Asia are expanding EV use in two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and affordable cars.
Global forecasts predict EVs could account for 30–40% of all car sales by 2030, thanks to falling battery costs and government policies.
Servicing & Maintenance
EVs require less upkeep than petrol cars due to fewer moving parts.
Typical Maintenance Needs:
- Battery health checks
- Tire rotation and brake inspection
- Cabin air filter replacement
- Occasional software updates
No oil changes, exhaust repairs, or complex engine overhauls are needed.
Models Available (Worldwide)
- Dongfeng: DFAC Dongfeng EM27, EV32
- Tesla: Model 3, Model Y
- Nissan: Leaf
- Hyundai: Kona EV, Ioniq 5
- BYD: Atto 3, Dolphin, e6
- MG: ZS EV
- Tata: Nexon EV
- Kia: Niro EV
- GWM (Great Wall Motors): Ora Good Cat
Future of Electric Vehicle
The coming years promise even more transformation:
- Solid-State Batteries: Higher range, faster charging, improved safety.
- Autonomous Driving: EVs will integrate self-driving systems seamlessly.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Cars will feed electricity back into the power grid.
- Affordable Options: By 2030, EVs are expected to cost the same—or less—than petrol cars.
- Green Charging Networks: Powered by renewable energy for truly sustainable transport.
Environmental Impacts of Electric Vehicle
Electric vehicle (EVs) Provides a substantial reduction in environmental pollutants when compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gases: A key advantage of EVs is their zero tailpipe emissions. This directly cuts down the release of carbon dioxide (CO?) and other pollutants, significantly improving urban air quality.
- Synergy with Renewable Energy: The environmental benefit of EVs is magnified when charged using renewable energy sources. In regions with clean grid infrastructure, their overall carbon footprint becomes minimal.
- Quieter Urban Environments: The silent operation of EVs contributes to reduced noise pollution, creating more peaceful conditions in cities and residential areas.
- Resource Recovery through Recycling: Advancements in technology allow for the recycling of lithium-ion batteries. Materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be recovered, which helps reduce the need for new mining operations.
Electric Vehicle: A Growing Market in Nepal
Nepal has a unique advantage in adopting EVs, thanks to its clean hydropower resources. Government policies, tax incentives, and private investments are making EVs increasingly popular.
Popular Electric Vehicle in Nepal:
- DFAC Dongfeng EM27, DFAC Dongfeng EV32
- MG ZS EV
- BYD Atto 3, Dolphin, e6
- Hyundai Kona Electric, Ioniq 5
- Nissan Leaf
- Tata Nexon EV
- Kia Niro EV
- Sundarijal K1 & Small City EVs (for urban driving)
Electric van Charging stations are expanding in Kathmandu, major highways, and border points, enabling wider adoption.
Explore More School van for sale and Price



.png)
.png)